Amid the eukaryotes, structure of a plant cell is unique as they can produce their own food and have membrane-surrounded nucleus and organelles. They can absorb sunlight and create carbohydrates and sugars as their food by convert carbon dioxide and water due to available Chlorophyll which also gives green color for plants.


Structure Of A Plant Cell: Microfilaments
Actin is globular proteins used to make these solid rods. These filaments are a significant part of the cytoskeleton and are mainly structural in purpose.
Mitochondria
It is organelle in oblong shaped located in the cytoplasm of every eukaryotic cell. It provides energy in plant cells by break down sugar and carbohydrate molecules to produce energy as long as there is light available for the chloroplasts.
Cell Wall
There is a rigid wall covering the plasma membrane in plant cells. However, this structure of a plant cell is far more intricate and serves in many different forms including keeping the plant organism to survive.
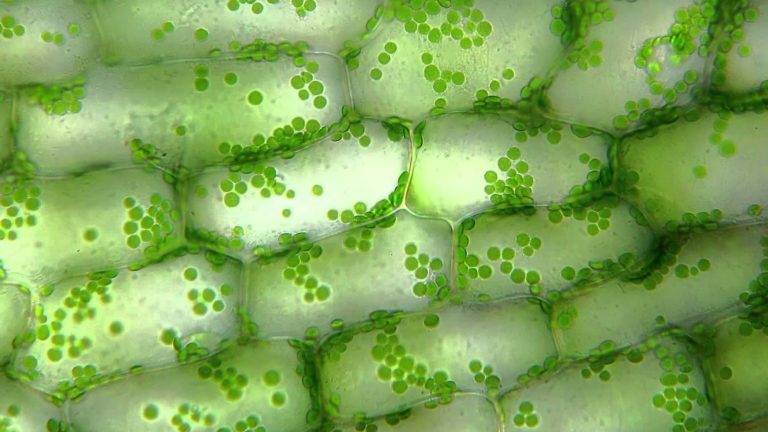
Chloroplasts
Photosynthesize is the most important unique ability of plants which help them to create chemical energy by converting light energy to make own food. Chloroplasts are specialized organelles to perform this process.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Chemical products are produced, processed, and sent in and outer of the cell via a network of pouches called the endoplasmic reticulum. Between the cytoplasm and the nucleus, there is a pipeline connecting to the dual-layered nuclear packet in structure of a plant cell. The plasmodesmata also connect the endoplasmic reticulum in plants.
Golgi Apparatus
The cell’s substance products are distributed and transported by the Golgi apparatus. It transports converted fats and proteins outside of the cell which are produced in the endoplasmic reticulum.
Microtubules
Its functions are to transport, as structural support and many other functions in structure of a plant cell and are located all over the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells in form of straight, void cylinders.
Nucleus
This organelle is highly specialized to control and process the information of the cell. Its major functions include keeping the cell’s DNA or genetic material and it manages the cell’s activities such as medium metabolism, growth, protein production, and cell separation (reproduction).
Peroxisomes
peroxisomes are the most common microbodies among other several types. A diverse group of organelles are called Microbodies and are located in the cytoplasm, generally sphere-shaped and tied by a single membrane.
Ribosomes
There is about 40 percent protein and 60 percent RNA in these tiny organelles called ribosomes found in all living cells. There are four strands of RNA in ribosomes in eukaryotes structure of a plant cell.